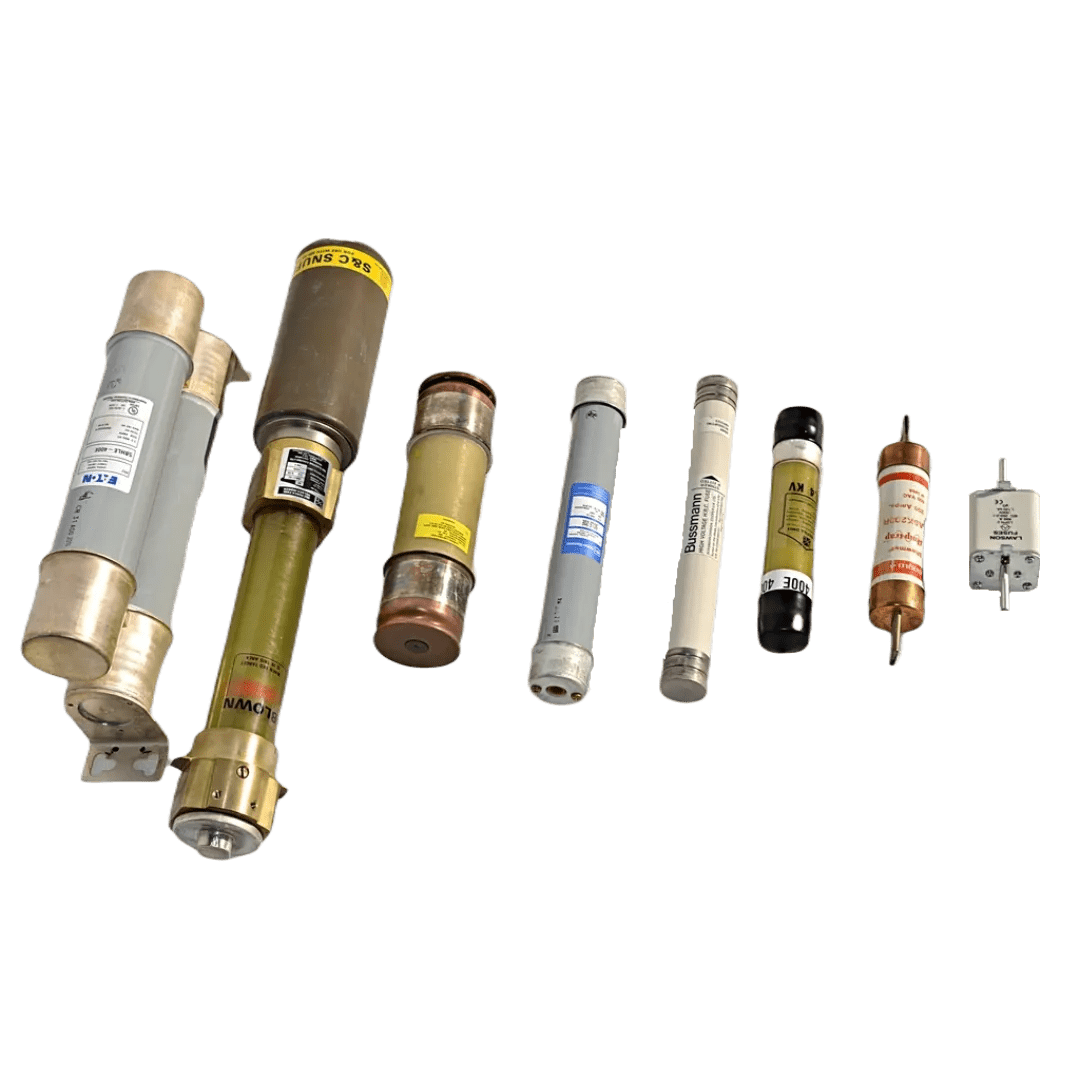
Electrical fuses are protective devices used in electrical systems to prevent damage from excessive current. Fuses are designed to interrupt the circuit by melting a metal wire or element when the current exceeds a certain threshold. This prevents overheating, fires, and damage to electrical equipment. Fuses are available in various ratings, sizes, and types, including cartridge, blade, and glass tube fuses. They are commonly used in residential, commercial, and industrial circuits to protect sensitive equipment like motors, transformers, and wiring systems. Fuses are one-time use devices and must be replaced when blown.
Key Features:
- Overload Protection: Disconnects the circuit in case of excessive current, preventing damage.
- One-Time Use: Designed to be replaced after they blow.
- Variety of Types: Includes cartridge, blade, and glass tube fuses for different applications.
- Compact and Reliable: Easy to integrate into electrical panels and systems.
Types and Standards:
- Cartridge Fuses: For industrial and motor protection.
- **Blade Fuses
**: Commonly used in automotive and electronic applications.
- Glass Tube Fuses: Used in low-voltage circuits and home appliances.
- **IEC 60269, UL 248: Standards for fuse construction and performance.
Brands Available:
Schneider Electric, Eaton, Siemens, Littelfuse, Bussmann.
General Maintenance:
Regularly inspect fuses for signs of failure or wear. Ensure that the fuse rating matches the circuit requirements. Replace blown fuses with the correct type and rating to ensure proper protection.